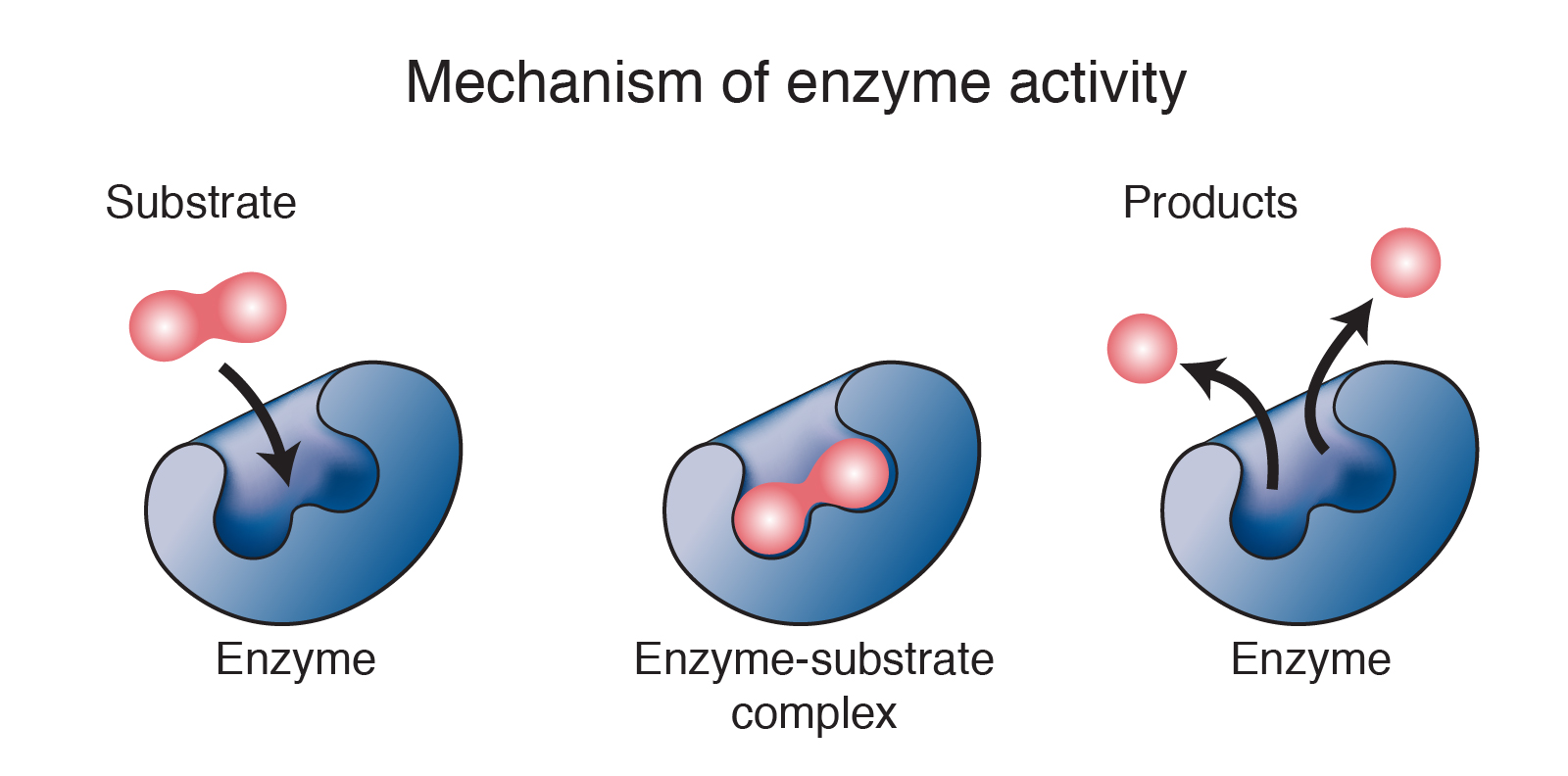
Enzymatic Chemical Reaction . In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. introduction to enzymes mechanisms.
from www.genome.gov
enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells.
Enzyme
Enzymatic Chemical Reaction a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or.
From bio.libretexts.org
6.7 Enzymatic Reaction Mechanisms Biology LibreTexts Enzymatic Chemical Reaction Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.albert.io
Enzymes AP® Biology Crash Course Review Albert.io Enzymatic Chemical Reaction enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. an enzyme is a substance that. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From studygripewater.z21.web.core.windows.net
Explain How An Enzyme Works Enzymatic Chemical Reaction a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. an. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From oerpub.github.io
This image shows the steps in which an enzyme can act. The substrate is Enzymatic Chemical Reaction In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. an enzyme is a substance that acts. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.worthingtonweb.com
Lipase Worthington Enzyme Manual Enzymatic Chemical Reaction In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From dxolxdkjo.blob.core.windows.net
Enzymatic Chemical Reaction Meaning at Janie Bourg blog Enzymatic Chemical Reaction a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.worthingtonweb.com
Superoxide Dismutase Worthington Enzyme Manual Enzymatic Chemical Reaction Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. a fundamental task. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] Provide a mechanism for the following enzymatic reaction Enzymatic Chemical Reaction Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. a fundamental task of proteins. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From pubs.rsc.org
Predicting enzymatic reactions with a molecular transformer Chemical Enzymatic Chemical Reaction an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. Most. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.worthingtonweb.com
Amylase, Beta Worthington Enzyme Manual Enzymatic Chemical Reaction In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From foodtechpathshala.com
Enzymatic Browning in Fruits & Vegetables FoodTech Pathshala Enzymatic Chemical Reaction introduction to enzymes mechanisms. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.researchgate.net
General type of reactions catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Other Enzymatic Chemical Reaction a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.youtube.com
General Biology 1 Components of an Enzyme YouTube Enzymatic Chemical Reaction enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being. a fundamental task of proteins is to. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From sciencestruck.com
Enzymatic Browning Science Struck Enzymatic Chemical Reaction Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. introduction to enzymes mechanisms. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From dxolxdkjo.blob.core.windows.net
Enzymatic Chemical Reaction Meaning at Janie Bourg blog Enzymatic Chemical Reaction Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.researchgate.net
Chemical and enzymatic reactions generating ROS and main antioxidant Enzymatic Chemical Reaction enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being. In the first step, an enzyme molecule (e) and the substrate molecule or. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From www.pinterest.ca
Enzymes Draw It to Know It Biochemistry, Teaching biology, Biology Enzymatic Chemical Reaction enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. enzymes are catalysts that drive reaction rates forward. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. Most catalysts, but not all, are made up of amino acid chains called proteins. . Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.
From biology4ibdp.weebly.com
2.5 Enzymes BIOLOGY4IBDP Enzymatic Chemical Reaction introduction to enzymes mechanisms. enzymes catalyze their reactions stereospecifically and are highly specific for their substrates. a fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within cells. an enzyme is a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which. Enzymatic Chemical Reaction.